Motion and Measurement of Distances, class 6, science
Motion and Measurement of Distances
- ·
In ancient times no means of transport were available people
mainly travel by foot and carry luggage on their back
- ·
after domestication of animals human being start using
horses, camels, elephants for transportation and carrying goods from one place
to another
- ·
after inventions of steam engine as a new power source it
lead to development of train, automobiles, motor ships as means of transport on
water and land
- · after the invention electricity electric trains, aeroplane are used as new mode of transportation
Measurement is the process of
comparing the unknown quantity of an object to be measured with a standard unit
of measurement
- · In
early Times people use parts of their body to measure the length of object
Conventional
Methods: They give approximate measurement.
I.
Handspan: Length between the tip of the thumb
and little finger
II.
Cubit:
It is the length between the tip of the middle finger and elbow.
III.
Arm
length: Length taken from shoulder to the tip of the middle finger.
IV.
Footstep: It is the distance covered in a
step.
Disadvantages:
Differed from person to person and lacked precision so this method is
inaccurate.
Standard unit of measurement are
those that have a fix quantity and their food do not very from person to person
and place to place
Standard
Units of Measurement: In
1960 scientist adopt uniform and conventional sets of standard unit for
measuring physical quantities.
·
this
system is known as international system of units or SI units
Some physical quantities are:
- ·
SI
unit of length is metre (m)
- ·
SI
unit of time is second (s)
- ·
SI
unit of mass is kilogram (Kg)
- ·
SI
unit of temperature is Kelvin (K)
Rules
For Writing Symbols Of Units
1.
Symbols for standard units are written in small letters.
2. Symbols are not written in the plural.
Each metre (m) is divided into 100
equal divisions, called centimetre (cm). Each centimetre has ten equal
divisions, called millimetre (mm). Thus
1 m = 100 cm
1 cm = 10 mm
For measuring large distances, metre is not a convenient unit. We define a
larger unit of length. It is called kilometre (km).
1 km = 1000 m.
Sub-multiples of units: Units used for measuring
smaller distances are the sub-multiples of SI units.
For example, milli, centi, deci.
1 m = 10 decimetre
1 m = 100 centimetre
1 m = 1000 millimetre.
Making
measurement of a length: In
making measurement of length of an object, we should follow the following
procedure:
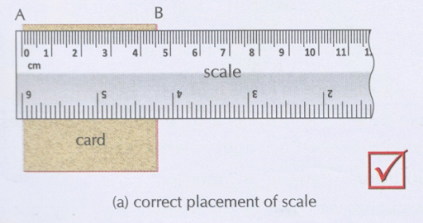
Place the scale in contact with the object along its length as shown in Fig.
Measurement with a scale with broken
ends
·
Avoid
taking measurements from zero mark.
·
Use
any other full mark of the scale, say 1.0 cm.
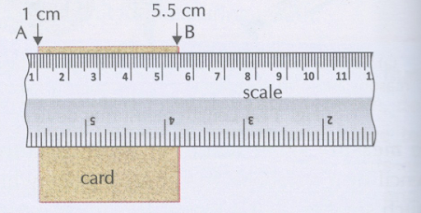
·
Subtract
the reading of this mark from the reading at the other end. For example, in Fig,
the reading at starting mark is 1.0 cm and at the other end it is 5.5 cm.
Therefore, the length of the object is (5.5 – 1.0) cm = 4.5 cm.
·
Correct position of the eye is also
important for making measurement. Your eye must be exactly above the point
where the measurement is to be taken as shown in Fig. 10.4. Position ‘A’ is the
correct position of the eye. Note that from position A’, the reading is 1.0 cm.
From positions ‘B’ and ‘C’, the readings may be different.
Least count: A scale is marked in
centimetres and millimetres. With the scales of this kind we can measure
correctly up to one millimetre, that is one-tenth of a centimetre. This is
called the least count of a (15 cm) scale.
Measurement Along Curved Line
Is it possible to
measure a curved line with a metre scale? Well, it is not so. Hence to measure
a curved line the following steps can be taken into account:
·
Take a thread and tie a knot at one end.
·
From this end measure a small portion of the curved line which
is somewhat straight and put the thumb.
·
Now again start from the thumb marked position and measure
another small portion of the line.
·
Repeat this process until you reach the end of the line.
Tie a knot on the thread on reaching the end. Now measure the two knots using a
metre scale.
Stationary objects: The object which do not move from its
position is known as stationary objects
Rest: Object said to be
at rest if it's position remain constant with respect to stationary object in
the surrounding
Motion: An object is said to be in motion
if it change its position with respect to stationery object in the surrounding
Rest and motion are relative terms for example and electric pole
appears to be at rest or stationary when we observe it by standing on the road
but the same pole appears to move when we observe from running train.
Types of motion: Types of motion for convention
motion of different object can be classify as
1.
Translatory
motion : when all the
parts of the board object move the same distance in given time then the motion
of an object is said to be translated motion
. for example
·
a
child going down a slide
·
a
vehicle moving on a road
Translatory
motion is are of two type: rectilinear
motion and curvilinear motion
·
a
car moving in a straight line
· ball falling from a roof
(b) Curvilinear motion: when an object move along a curved line called curvilinear motion for example
·
a
car moving along a curve path
·
a
ball is thrown by a boy second
(2) Circular motion: when ana object
moves along a circular path, it is said to be circular motion. For example
·
motion
of the moon around the earth
·
running
of athlete in a circular track
(3) Rotatory motion: object is said to be in rotatory motion
if it moves about a fix Axis without changing its position. for example
·
the
motion of laid of fan spinning wheel
·
merry
go round
(4) Oscillatory motion: when
and object move to-and-fro about its mean position, its motion is called
oscillatory motion.for example
·
motion
of swing
·
motion
of pendulum
(5) Vibratory motion: a
motion in which a part of object remain fixed and do not move while the other
part of object move to-and-fro in a definite pattern is called vibratory motion
for example
·
Guitar
·
drum
(6) Periodic motion: the
motion that ready repeat itself after regular interval of time is called
periodic motion for example
·
swinging
pendulum of wall clock
·
needle
of machine
·
heartbeat
·
motion
of Earth
(7) Non- Periodic motion: the
motion that does not repeat itself at regular interval is called Non- Periodic motion.
Note- Sometime a body can possess more
than one types of motion at the same time such type of motion is called
multiple motion. For example
·
a
boy writing a bicycle here the wheels of the bicycle rotate and at same time it
move in a straight path so it have rotatory and rectilinear motion
·
Earth
rotate about the sun so it have circular motion as well as rotatory motion because
it rotate about its axis.







Comments
Post a Comment